Cell: Structure and Functions
Chapter Overview
This chapter introduces the basic unit of life, the cell. It explains the structure and functions of different cell components, types of cells, and their organization in living organisms. Students will learn about the differences between plant and animal cells, the discovery of the cell, and the significance of cells in biology.
Cell: The smallest structural and functional unit of an organism, which is typically microscopic and consists of cytoplasm and a nucleus enclosed in a membrane.
Discovery of the Cell
The cell was first discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665 when he observed a thin slice of cork under a microscope. He noticed small compartments resembling honeycomb structures and named them "cells." Later, scientists like Anton van Leeuwenhoek observed living cells.
Cell Theory
The cell theory, formulated by Schleiden, Schwann, and Virchow, states:
- All living organisms are composed of cells.
- The cell is the basic unit of life.
- All cells arise from pre-existing cells.
Types of Cells
Cells can be classified into two types based on their structure:
- Prokaryotic Cells: Simple cells without a well-defined nucleus (e.g., bacteria).
- Eukaryotic Cells: Complex cells with a well-defined nucleus (e.g., plant and animal cells).
Structure of a Cell
A cell consists of three main parts:
- Cell Membrane: A thin, flexible outer covering that controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
- Cytoplasm: A jelly-like substance where cell organelles are suspended.
- Nucleus: The control center of the cell that contains genetic material (DNA).
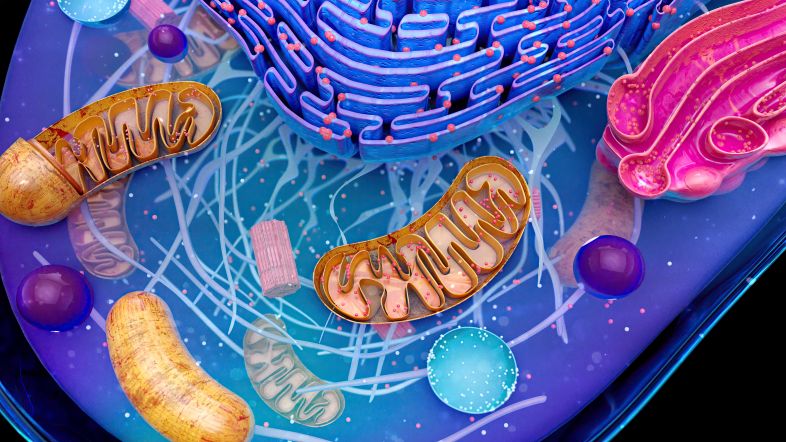
Cell Organelles
Key organelles in a eukaryotic cell include:
- Mitochondria: Powerhouse of the cell, produces energy (ATP).
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): Helps in protein and lipid synthesis.
- Golgi Apparatus: Packages and transports materials.
- Lysosomes: Digestive enzymes that break down waste.
- Chloroplasts: Found in plant cells, site of photosynthesis.
- Vacuoles: Storage sacs for water and nutrients.
Differences Between Plant and Animal Cells
| Feature | Plant Cell | Animal Cell |
|---|---|---|
| Cell Wall | Present (made of cellulose) | Absent |
| Chloroplasts | Present | Absent |
| Vacuoles | Large and central | Small and numerous |
Functions of the Cell
Cells perform various functions essential for life, including:
- Growth and reproduction
- Energy production
- Protein synthesis
- Waste elimination
- Response to stimuli
