Chapter Overview
This chapter explains the concept of gravitation, first introduced by Sir Isaac Newton. It covers the Universal Law of Gravitation, free fall, acceleration due to gravity, and differences between mass and weight. It also explores buoyancy, the role of gravity in planetary motion, and real-life applications.
Important Keywords
- Gravitation: The force of attraction between two bodies due to their masses.
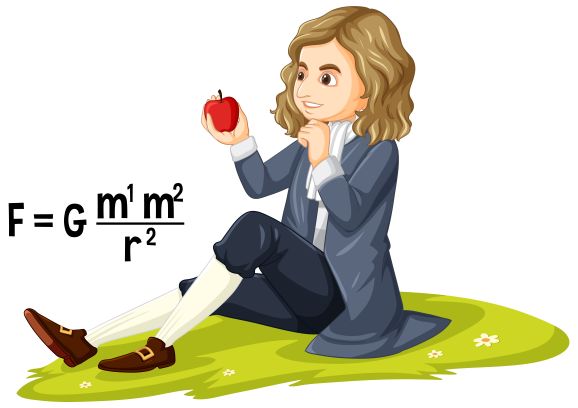
- Universal Law of Gravitation: Every object attracts every other object with a force proportional to their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
- Acceleration due to Gravity (g): The acceleration experienced by an object due to Earth's gravity (9.8 m/s²).
- Free Fall: Motion of an object under the influence of gravity alone.
- Mass: The amount of matter in an object, constant everywhere.
- Weight: The force exerted by gravity on an object (W = mg).
- Buoyancy: The upward force exerted by a fluid on an immersed object.
- Density: Mass per unit volume (ρ = m/V).
